Fundamentals of Physical Geography
UNIT I : GEOGRAPHY AS A DISCIPLINE
“What is geography”? In very simple words, it can be said that geography is the description of the earth. The term geography was first coined by Eratosthenese, a Greek scholar (276-194 BC.). The word has been derived from two roots from Greek language geo (earth) and graphos (description).
UNIT II : THE EARTH
This unit deals with –
Origin and evolution of the earth; Interior of the earth; Wegener’s continental drift theory and plate tectonics; earthquakes and volcanoes
Chapter-2
The Origin and Evolution of the Earth
Galaxies form from nebulae. Dark matter plays a crucial role in their formation. Stars are born within nebulae.
Chapter-3
Interior of the Earth
Scientists study the Earth’s interior through indirect methods like seismic waves and analysis of surface materials. Direct observations are limited to the Earth’s crust.
Chapter-4
Distribution of Oceans and Continents
Scientists now understand that the Earth’s surface and interior are dynamic, with tectonic plates moving due to convection currents. These currents are driven by heat from radioactive decay and residual heat within the Earth.
UNIT III : LANDFORMS
This unit deals with –
Landforms and their evolution, Geomorphic processes — weathering, mass wasting, erosion and deposition; soils — formation
Chapter-5
GEOMORPHIC PROCESSES
Our earth is a playfield for two opposing groups of endogenic and exogenic geomorphic processes
Chapter-6
Landforms and their Evolution
Several related landforms together make up landscapes.
Each landform is a result of the action of geomorphic agent.
UNIT IV : CLIMATE
Atmosphere — compositions and structure; Insolation; Temperature — factors; Pressure belts; Winds and air masses and fronts; tropical and extra tropical cyclones; Precipitation types; World climates classification (Koeppen), greenhouse effect,
global warming and climatic changes

World Climate and Climate Change : (Project presentation only)
CHAPTER-11
Unit-V Water (Oceans)
Chapter-12
Water (Oceans)
The diverse underwater terrain of ocean from the shallow continental shelf to the deep trenches and mid-ocean ridges.
Chapter-13
Movements of Ocean
Ocean water is dynamic. The horizontal and vertical motions are common in ocean water bodies
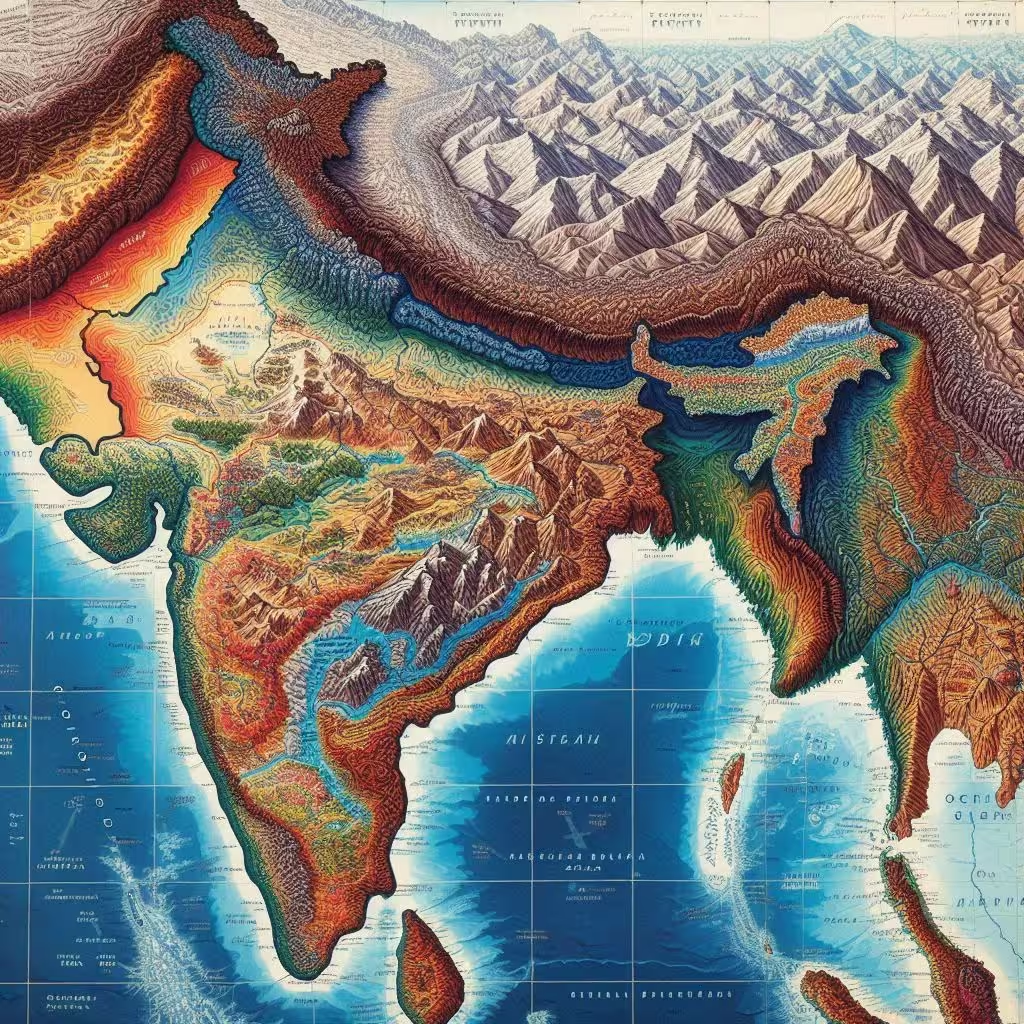
INDIA – PHYSCIAL ENVIRONMENT
India — Location, Structure and Physiography, Drainage System, Climate, Natural Vegetation